A complete introduction to fiber optic connector types/single-mode and multi-mode specifications/application distances/fusion splicing methods

Image by Beautiful optical fiber detail- www.freepik.com
Have you ever wondered how an email can be sent from Taiwan to the rest of the world in just one second? In our daily lives, from uploading photos and watching videos online to undergoing endoscopic examinations in hospitals and even international communications, behind all of this, there is actually a thread thinner than a hair───「Fiber optics」.
「Fiber optics」has become a critical technology, widely used in science, communications, industry, and other fields. At Longzhong, we offer a comprehensive guide to fiber optics. Today, we'll introduce this world-changing transmission medium.
Next, we'll explain the principles of optical fiber, comparing its advantages and disadvantages, fiber materials and transmission quality, the differences between single-mode and multimode, application distances, fiber's applicable environments and scenarios, fiber connector types, and more. This will provide you with a clear understanding of optical fiber characteristics and help you choose the components that best meet your needs.
What is optical fiber? How does optical fiber work?
Fiber optics is a transmission technology that utilizes optical principles. Light travels extremely quickly through the core of an optical fiber, leveraging the properties of total internal reflection between different materials to rapidly transmit signals and data.
Due to its susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, low loss, and long-distance transmission capabilities, fiber optics are widely deployed in cities and on the ocean floor, enabling high-speed, efficient, and stable communications for human life.
Advantages and disadvantages of optical fiber
● Advantages of optical fiber:
1. Extremely fast transmission speeds
The speed of light is nearly 300,000 kilometers per second, enabling rapid processing of large amounts of data.
2. Long transmission distance
Optical fiber has very little signal attenuation and does not require frequent signal reinforcement, allowing transmission over tens or even hundreds of kilometers (especially single-mode fiber).
3. Anti-electromagnetic interference
Optical signals are not affected by electromagnetic or radio waves.
4. High Security
Fiber optic transmission does not emit electromagnetic waves into the external space, making it difficult to intercept, making it suitable for transmissions requiring high confidentiality.
● Disadvantages of optical fiber:
1. High Maintenance Costs Fiber optic cable installation requires specialized tools and personnel, making maintenance less straightforward than traditional copper cables.2. The inner core is relatively fragile and unusable if damaged. Fiber optic cables are made of glass or plastic and are sensitive to bending, pulling, and vibration, requiring special care during transportation and installation.
3. No Power Supply Fiber optic cables only transmit light and cannot simultaneously supply power like coaxial cables or twisted-pair cables. Therefore, if your device requires power, separate wiring is required.

Fiber material / transmission quality / application distance / applicable environment and scenarios
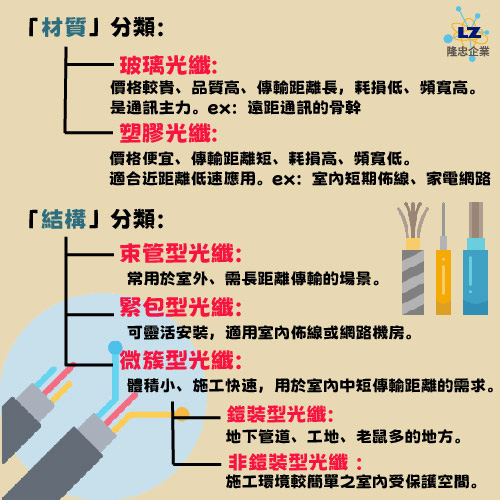
Fiber optics are classified by their material:
● Glass fiber: More expensive, high quality, long transmission distance, low loss, and high bandwidth. It's the backbone of communications, e.g., long-distance communications.
● Plastic fiber: Cheaper, shorter transmission distance, high loss, and low bandwidth. Suitable for short-distance, low-speed applications, e.g., indoor short-distance wiring/home grid connections.
Fiber optic cables are categorized by their structure:
● Tube-type fiber: Commonly used for outdoor applications requiring long-distance transmission.
● Tight-buffered fiber: Flexible installation, suitable for indoor wiring or network rooms.
● Microcluster fiber: Small in size and quick to install, typically used for short to medium-distance transmission indoors.
Micro-cluster fiber can be further categorized based on environmental selection criteria:
● Armored fiber: Suitable for underground pipelines, construction sites, and areas with high rodent populations (metal or reinforcement layers, such as steel wire, are used to protect against rodent damage).
● Unarmored fiber: Suitable for low-risk, protected indoor spaces with simpler construction environments.
Single-mode fiber / multimode fiber comparison
Single-mode fiber: With a core diameter of only 8-10 microns, the fiber can accommodate only a single beam of light, with a wavelength of approximately 1300nm-1550nm. This allows light to travel tens of kilometers along a single-mode fiber. With the use of repeaters and other related equipment, transmission distances can be extended to hundreds of kilometers. However, due to its high precision, its manufacturing cost is relatively high, and it is primarily used for long-distance communications and high-speed data transmission.
● Multimode fiber: It has a core diameter (50-100 microns) that can accommodate multiple light beams transmitted simultaneously. The wavelength of light is usually 850nm-1300nm. The larger diameter makes multimode fiber less expensive, but it also limits its transmission distance and speed. It is only suitable for applications with short distances and medium bandwidth requirements. Multimode fiber is also divided into OM1-OM5 specifications based on its core diameter and effective bandwidth.。
Fiber optic connector types

LC fiber optic connector(Lucent Connector)
Used to connect SFP optical modules. The interface can be clipped onto the optical module. Uses 1.25mm diameter fiber ferrules and is typically used in single-mode fiber applications.

SC fiber optic connector(Standard Connector)
This push-pull connector uses a 2.5mm diameter fiber ferrule. Most commonly used on routers and switches, it is also a common connector for fiber optic cables, commonly used in single-mode and multimode applications.

ST fiber optic connector(Straight Tip Connector)
The interface is snap-on and is usually used in multimode applications and is also commonly used in fiber optic distribution frames.

FC fiber optic connector(Ferrule Connector)
Similar to the ST connector, this connector uses a threaded connection, providing a secure connection to the optical module. It is relatively uncommon today, typically used in single-mode applications, and is most commonly found in patch panels.
接頭.jpg)
MTP/MPO Fiber optic connector(Multi-fiber Pull Off)
It can accommodate 12-24 core optical fibers and is used for data transmission requiring high speed and high bandwidth, and is usually used in computer rooms.
Fiber fusion splicing method
● PC (Physical Contact)
PC is the most direct connection method, ideally allowing direct contact between the fiber cores and minimizing air gaps. However, in reality, it's difficult to achieve absolute zero-error levelness and flatness, making it suitable only for transmitting traditional single-mode and multimode fiber optic signals.
● UPC(Ultra Physical Contact)
PC's improved splicing method features a finer, smoother polish and curved splice surface, allowing only the essential core to be spliced. This significantly reduces errors caused by large, uneven splices, resulting in lower reflections and insertion loss. It is used in single-mode fiber, data transmission, and digital telecommunications systems (such as FTTH and data centers).
● APC (Angled Physical Contact)
APC offers the lowest reflection loss and is the optimal fiber-to-fiber splicing method for applications requiring highly stable signal transmission (e.g., medical, industrial, energy monitoring, etc.). This prevents reflected light from returning directly to the source and instead refracts into the cladding, dissipating the reflected light without affecting the original optical signal. APC must be connected end-to-end, and careful attention must be paid to the angle, otherwise significant optical loss will occur.
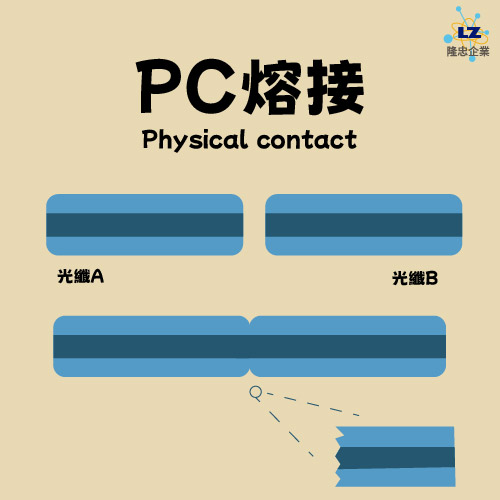
It is the most direct connection method and is only suitable for transmitting traditional single-mode and multi-mode optical fiber signal connections.

Improved PC splicing method for single-mode optical fiber, data transmission, and digital telecommunication systems (e.g., FTTH, data centers).
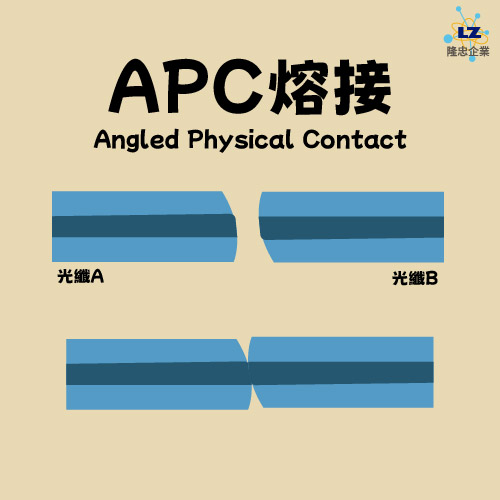
The return loss is the lowest, which is suitable for signal transmission requiring very high stability (for example: medical, industrial, energy monitoring).
Longzhong does not specialize in laying fiber optic cables, but can handle the piping and wiring required for electrical and instrumentation projects. Based on years of accumulated experience in electrical and instrumentation, Longzhong engineers will select the most suitable fiber optic cables and materials based on the owner's on-site environment and needs.
Any requirements for instrumentation and electrical integration, instrumentation installation
Longzhong provides Technical consulting services | Telephone: 06-243-7822

